WebAR for Chrome And Safari vs Mobile AR
Suppose you have an idea for an AR-enabled app. It is going to change the world and make you lots of money. Now you just need to decide on how exactly to implement these cool augmented reality features. The thing is, there are meaningful differences between WebAR for Chrome and Safari and mobile AR. And in this article, we will show them and give some advice on when to use which.


Mobile AR
Mobile AR covers augmented reality functionality that is included in a mobile app. It mostly operates on smartphones and tablets. Technically, the relevant software written for smart glasses also counts as mobile AR. But these devices are mostly used in industrial or military settings and so are out of this article’s scope.
Web AR
Web AR is augmented reality that is built into a web application. It takes the video feed from a webcam and displays it, with the attached AR effects, in a browser. WebAR for Chrome and Safari is supported by Google and Apple through WebXR and ARKit. However, there are a lot of third-party SDKs (software development kits) that also allow working with these browsers.
Web AR works on both mobile devices and desktop/laptop computers.
Speaking about browsers, we will focus on Chrome and Safari. On desktop computers, the browser from Google dominates, taking 68% of the market, while its Apple-built counterpart comes second with 9,5%. On mobile devices, the situation is similar: Chrome’s market share is 63%, and Safari holds 24,3%. The rest of the browsers stay below the 10% line in both mobile and desktop markets.
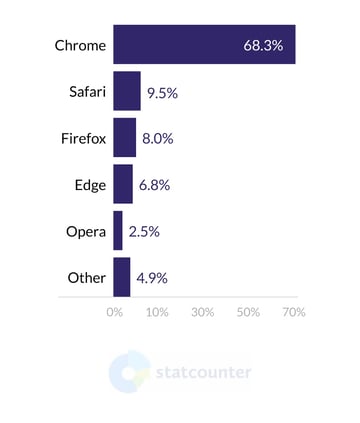 Desktop Browser Market Share Worldwide, July 2020 - July 2021. Statcounter
Desktop Browser Market Share Worldwide, July 2020 - July 2021. Statcounter
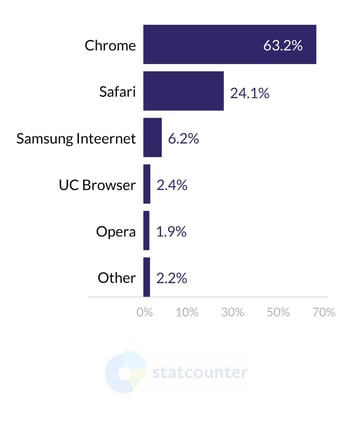 Mobile Browser Market Share Worldwide, July 2020 - July 2021. Statcounter
Mobile Browser Market Share Worldwide, July 2020 - July 2021. Statcounter
WebAR for Chrome and Safari vs Mobile AR
Now, let’s take a look at the factors you need to consider when choosing whether to go with mobile or web AR.
Device compatibility
As stated previously, web AR works on pretty much any internet-connected device with a browser and a webcam. Mobile AR, however, requires the device to support the technology, which means certain older models can’t use these features.
The compatibility depends on both the smartphone model and the software that the AR is based on. For example, our Face AR SDK works with iPhones starting from 6S and newer and covers about 80% of Android devices. It also supports webAR for Chrome, Safari, and other major browsers.
To sum it up, web AR offers the best accessibility, while mobile AR has somewhat higher requirements.

Audience size and reach
This directly ties in with the previous point. A web app can reach anyone if they have Chrome, Safari, or other popular browsers. Meanwhile, iOS has about 26.5% of the market, and Android - ca. 72%.
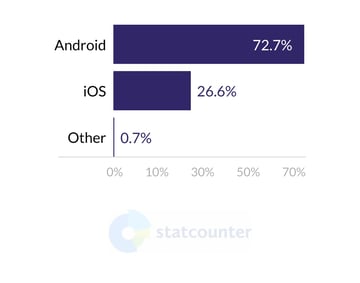 Mobile Operating System Market Share Worldwide, July 2020 - July 2021. Statcounter
Mobile Operating System Market Share Worldwide, July 2020 - July 2021. Statcounter
The reach of Web AR is 100%. The reach of a mobile app for each platform is a bit lower than the market share because older smartphones might not support AR.
Screen size
Certain tasks are much more convenient to execute when you have a larger screen. For example, creating and modifying virtual humans on a smartphone is a bit frustrating, even though the technology allows this.
Other things, like virtual makeup try-on, can work fine on web, mobile, and even in-store “smart mirrors”.
Before choosing web or mobile AR, take the screen size into account, as it can make or break the user experience.

Performance
All other things being equal, web AR offers worse performance and image quality than its mobile counterpart. It operates from the browser sandbox that gets resources from the device and that, in turn, allocates some of the CPU and GPU power to the AR application. As a result, having another app or a large video opened in a different tab will likely cause frame rate drops and lags.
Mobile apps, on the other hand, can use more resources and thus provide a better image.
Costs
Web AR for Chrome, Safari, Opera, and other browsers is, in fact, a single application adapted to multiple browsers. This is not the case for mobile AR. Even if you use React Native or Flutter to save on the development time, you still get two apps that need to be supported. Improving and updating both costs more.
In addition, the cost-per-acquisition is lower for web applications. The rule of thumb is that the fewer actions the user needs to take, the better. In the case of Web AR, people just need to visit the website, no downloads or later updates are required. So the marketing becomes more cost-effective, as more users interact with the app and per dollar invested.
That is not to say that you can’t use both mobile and web applications.

App Store Relations
Mobile apps are usually distributed through app stores: Apple App Store, Google Play Market, and Amazon App Store. Each of them has a stringent set of guidelines. This means you have to invest time and money in complying with the requirements - otherwise, your app won’t be allowed on the platform. The initial publishing can take an entire week, which is frustrating and expensive. Reviews of the updates take less time but whenever you release a new version there would be a certain lag due to the app store check.
Moreover, some apps (e.g. alcohol- and tobacco-related) cannot be released on App Store or Google Play at all.
Web AR doesn’t have such an issue. You control your website and can publish whatever you want. For example, if you need an AR-enabled advertisement for your high-end whiskey, the web is the way to go.
Offline mode
Web AR cannot work without an internet connection. Mobile AR, however, can. Moreover, even the features that require a user to be online, can be made to work without the internet. For example, saving a social media post/video and uploading it when the connection is restored.
How an AR SDK fits into this?
The easiest way to implement augmented reality features in your web or mobile application is to use an SDK - a premade module containing the said functionality. It can be integrated within a day while developing AR features from scratch could take many months.
Banuba Face AR SDK is focused on augmented reality that works with face recognition and modification. This includes:
- Beautification. Smoothing the skin, evening out its tone, removing wrinkles, acne, and blemishes, etc.
- Face filters. Augmented reality masks and stickers, on par with the ones in TikTok or Snapchat.
- Virtual makeup. Applying powders, lipstick, nail polish, and other cosmetic products.
- AR try-on. Realistically fitting hats, jewelry, eyeglasses, piercing, and the like.
- Face morphing. Changing the size and shape of facial features for a comical effect.
- Background replacement. Filtering out person and replacing the rest of the image with an image or 3D environment.
- Avatars. Animated 3D objects that move in accordance with the user.
- LUTs (Instagram filters). Color change for the entire picture and video.
The SDK supports mobile AR (native iOS and Android, as well as React Native and Flutter) and WebAR for Chrome and Safari, thus covering pretty much all screen sizes.
It can operate both online and offline. This includes the AR cloud option: storing certain effects and downloading them when the user actually needs them. A single mask could take 1-3 MBs of space, so AR cloud could be a great compromise that allows decreasing the app size while keeping the effects range varied.
Conclusion
Both mobile and web AR are viable options for AR-powered applications. Mobile AR offers better performance/image quality and can work offline. Web AR for Chrome and Safari can work on more devices, is cheaper to maintain, and is better suited for larger screens.
Mobile and web AR can be quickly and easily implemented by using an augmented reality SDK. And if you need augmented reality effects on people’s faces (makeup try-on, face filters, and so on), go ahead and try Banuba Face AR SDK. It has 14 days of free trial to see whether it is the right fit for you.





